The growth of non-religion will create a significant source of polarization. Many Americans are leaving religion behind (as I discussed previously). This will exacerbate social conflict, as we sort ourselves into religious and non-religious camps.
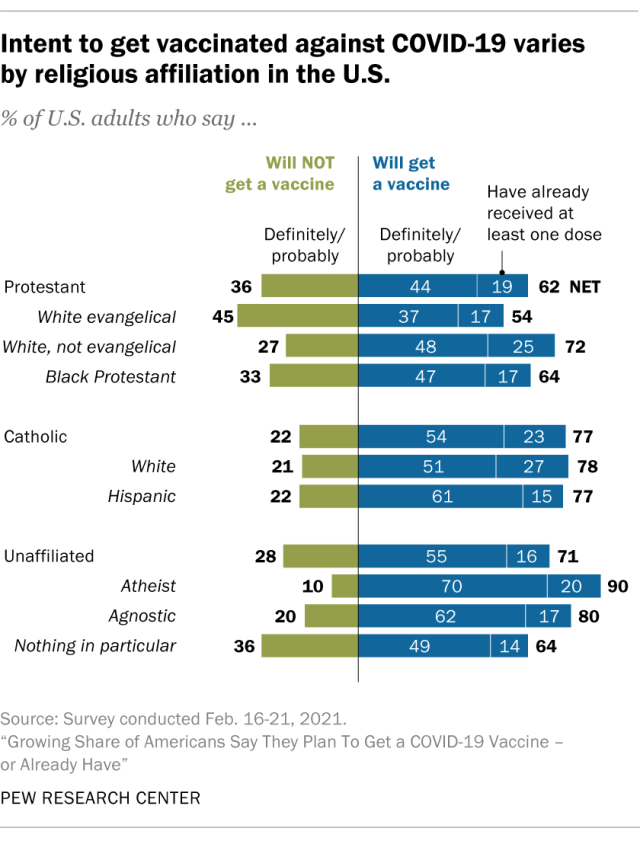
Consider, for example, polling data that shows that atheists are more likely to get a Covid-19 vaccine than evangelical Christians. 90% of atheists say they will get vaccinated, while only 54% of white evangelicals will do so.
This makes sense: atheists tend to trust science and medicine, while evangelicals do not. A similar result has been found with regard to climate change: atheists tend to be more engaged and alarmed about climate change than Christians who read the Bible literally.
But let’s be careful about overgeneralizing. Atheism can be as fragmented as the rest of society. Religion also contains a multitude.
And yet, the tendency to oversimplify is common. Theists sometimes simplistically dismiss atheism as the work of the devil. Atheists also dismiss theism in simplistic terms. But when it comes to religion and non-religion, complexity is the rule. Oversimplification obscures much that is important and interesting. It also prevents us from finding common ground.
Consider a recent skirmish among atheists. Richard Dawkins, a prominent atheist, posted a tweet appearing to disparage transgender people. Some atheists were appalled. The American Humanist Association publicly disavowed Dawkins and retroactively withdrew a “Humanist of the Year” award they gave him in 1996. Other prominent atheists leapt to Dawkins’ defense including Daniel Dennett, Sam Harris, and Steven Pinker. This provoked further backlash among atheists, with some accusing contemporary atheism of being a bastion of white male privilege.
This reminds us that atheism is not a monolith. Like everyone else, atheists have intersectional identities. Atheists can be Black or white, straight or gay, trans or cis, rich or poor. The same is true, of course, for religious people. Some religions embrace LGBTQ people. Others do not. Some religions embrace science, medicine, and Covid-19 vaccines. Others do not.
Generalizations about religion and non-religion are only vague approximations. Consider, for example, how atheism is colored by the religion that it rejects. It makes sense to ask whether a nonbeliever is a Christian atheist, a Muslim atheist, a Sikh atheist, a Jewish atheist, and so on. Some atheists want to avoid this complexity and state that they do not believe in any God or gods at all. But the binary logic of God or no God oversimplifies. It also helps to know which God and which tradition.
One could reject Christian or Muslim dogma, for example, while remaining culturally attached to Christianity or Islam. A culturally Christian atheist could enjoy the hymns and rituals of Christian holidays while also turning to the Bible for spiritual insight. Or an atheist with Muslim roots could fast during Ramadan. Things become even more complicated when religious identity is connected to ethnic identity—as in Judaism or in the diverse indigenous religions of the world.
Scholars have also pointed out that self-identification as an atheist depends on social privilege. Member of racial and ethnic minorities are less likely to publicly identify as atheist. This is not simply a matter of what people believe. It is also connected to the social need to be more (or less) closely identify with a religious tradition. White men may find it easier to affirm atheism than Black women or members of native American tribes.
These issues are intriguing and they will likely become more complicated and intense as non-religion grows. As more people leave religion behind, the diversity of the non-religious will grow.
Celebrating diversity among nonbelievers may in turn lead more people to leave religion behind, especially those who self-identify in nontraditional ways. One worry about this possibility, however, is that it may leave religious congregations more homogeneous than they already are, further increasing polarization.
Perhaps there will be some convergence among the non-religious. The fact that 90% of atheists plan to get vaccinated points in that direction. But despite convergence around science, increasing diversity will pose a challenge for the broad community of non-belief.
We find ourselves in the middle of an unprecedented experiment in secularization. Let’s keep our minds and hearts open. Let’s try to resist increased polarization and avoid oversimplifying the complex rainbow of human experience.



